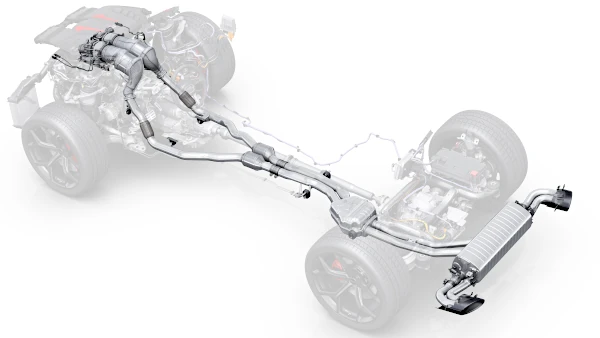
Exhaust System in Cars: Structure, Function, and Importance
The exhaust system in a factory-built car with an internal combustion engine plays a key role in discharging exhaust gases, reducing noise, and minimizing harmful emissions. Thanks to innovative technologies like catalytic converters, particulate filters, and turbochargers, modern exhaust systems are not only more efficient but also more eco-friendly. This article presents the main components of the exhaust system and their functions.
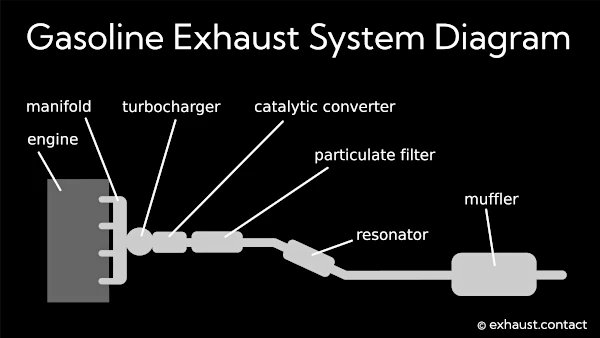
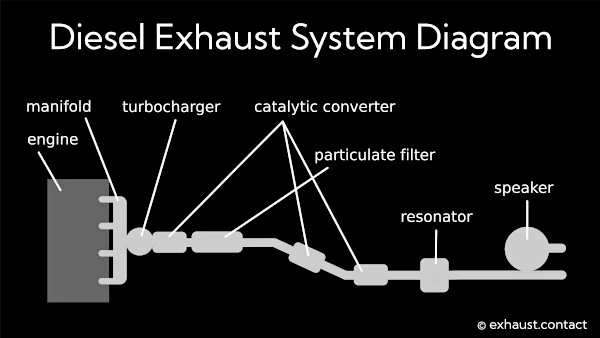
1. Exhaust Manifold
The exhaust manifold is the first component of the exhaust system, directly connected to the engine's cylinder head. It collects exhaust gases from the cylinders and directs them to the subsequent parts of the system. Typically made of cast iron or stainless steel, it is designed to withstand high temperatures.
2. Turbocharger (if present)
In cars equipped with a turbocharger, exhaust gases pass through a turbine that drives an air compressor. The compressed air is then forced into the cylinders, enhancing the car’s performance. Additionally, it helps reduce exhaust noise.
3. Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter is one of the most critical components of the exhaust system, responsible for reducing harmful emissions. Through chemical reactions, it converts nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrocarbons (HC) into less harmful substances such as nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O).
The SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) system, increasingly used in diesel passenger cars, reduces NOx emissions by injecting a urea solution (AdBlue).
4. Filters in the Exhaust System
Modern cars are often equipped with filters that reduce harmful particle emissions:
- DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter): Uses a process to burn off soot and ash particles in diesel exhaust systems.
- GPF (Gasoline Particulate Filter): Functions similarly to the DPF but is designed for gasoline engines.
- FAP (Filtre à Particules): Used in French car brands like Peugeot and Citroën to capture particulate matter.
5. Sensors in the Exhaust System
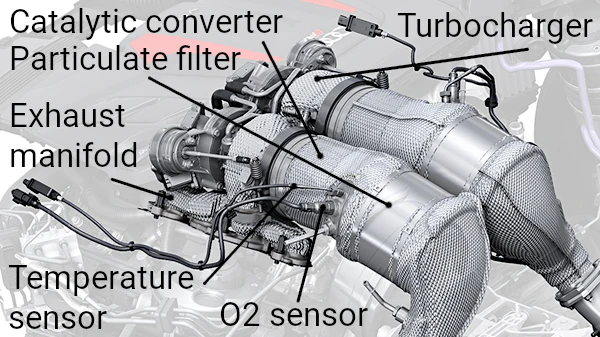
The exhaust system is equipped with various sensors connected to the vehicle's computer. Based on their readings, the fuel injection and ignition are regulated:
- Lambda Sensor: Measures the oxygen content in exhaust gases and helps optimize the air-fuel mixture.
- Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor: Protects exhaust components from overheating.
- NOx Sensor: Measures nitrogen oxide levels, especially in vehicles with SCR systems.
6. Valves in the Exhaust System
Valves control exhaust flow and can affect efficiency, emissions, and sound:
- EGR Valve (Exhaust Gas Recirculation): Recirculates a portion of exhaust gases to help reduce NOx emissions.
- Exhaust Flap: Regulates exhaust flow, affecting engine power and noise levels.
7. Resonator
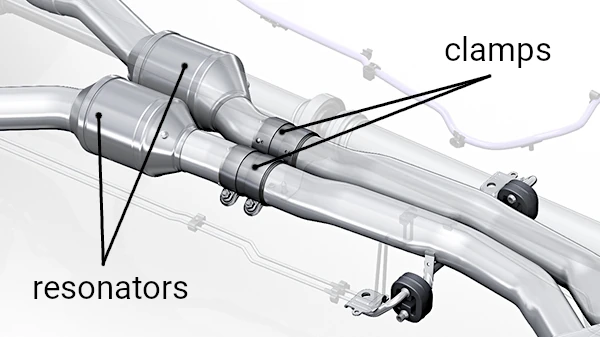
The resonator tunes the sound of the exhaust system by eliminating a narrow range of unwanted frequencies. It primarily uses acoustic resonance, reflecting sound waves to cancel them out.
8. Muffler
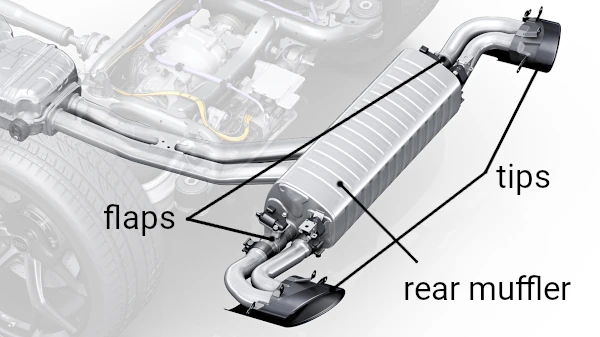
The muffler reduces the noise generated by exhaust gases. It features chambers and baffles and may include sound-absorbing materials (less common in factory exhaust systems) that dissipate acoustic waves and lower noise.
9. Exhaust Pipes
Exhaust pipes are vital components that connect various parts of the exhaust system and direct exhaust gases out of the vehicle. Their design significantly impacts the engine's performance, fuel efficiency, and exhaust sound.
Pipes come in various shapes and sizes, including straight, bent, or oval designs, tailored to fit the vehicle's layout and optimize gas flow. The diameter and length of the pipes are crucial in determining backpressure, which influences engine efficiency and power delivery.
Flexible joints, often made of stainless steel or other heat-resistant materials, are commonly used in exhaust systems to accommodate vibrations and thermal expansion. These components enhance durability and prevent damage to other parts of the system.
10. Exhaust Tip
The exhaust tip is the visible part of the exhaust system on the outside of the vehicle. Its shape and material influence aesthetics and slightly affect the sound of the exhaust system.
11. Isolators, Gaskets, and Clamps
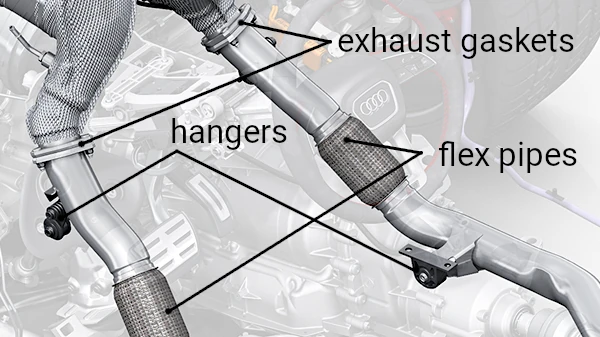
Isolators, gaskets, and clamps are essential accessories in an exhaust system, ensuring a secure, efficient, and noise-free connection between its components. These parts play a crucial role in maintaining the system’s integrity and performance over time.
Exhaust Isolators / Hangers
Exhaust isolators / hangers, often made from durable rubber or polyurethane, are used to suspend the exhaust system and absorb vibrations caused by engine operation. They prevent metal-on-metal contact, reducing noise and protecting components from wear and tear. Isolators are critical for minimizing stress on exhaust pipes and maintaining proper alignment.
Gaskets
Gaskets are used to create airtight seals between various parts of the exhaust system, such as the manifold and the catalytic converter or between flanges. Made from materials like high-temperature-resistant metal or composite fibers, gaskets prevent exhaust gas leaks, which could reduce system efficiency and increase emissions.
Clamps
Exhaust clamps are used to secure connections between pipes, ensuring they remain tightly joined even under the high temperatures and pressures of exhaust operation. Available in different types, such as U-bolt clamps, band clamps, and V-band clamps, they provide flexibility for repairs or modifications while maintaining a strong seal.
Additional Accessories
Various accessories can enhance the performance and maintenance of an exhaust system:
- Heat Shields: Protect surrounding components from the high temperatures of the exhaust pipes and improve safety.
- Exhaust Wraps: Insulating wraps that help retain heat within the pipes, improving exhaust flow and reducing heat exposure in the engine bay.
- Sealants: High-temperature sealants can be applied at joints to provide an additional layer of sealing against leaks.
Proper selection and maintenance of isolators, gaskets, clamps, and accessories ensure that the exhaust system operates efficiently, quietly, and safely for the vehicle’s lifetime.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions About the Exhaust System
- What are the symptoms of an exhaust system failure? Common symptoms include a louder engine noise, reduced power, increased fuel consumption, and the smell of exhaust gases inside the cabin.
- What is a DPF filter, and why is it important? The DPF filter captures soot particles produced during combustion. Its purpose is to reduce exhaust emissions and protect the environment.
- How to care for a catalytic converter? To prolong the catalytic converter's lifespan, ensure regular vehicle maintenance and avoid short trips that do not allow it to regenerate fully.
- Can I remove the catalytic converter? Removing the catalytic converter is illegal and increases exhaust emissions. In many countries, it is subject to financial penalties.
- What is the difference between a muffler and a resonator? The muffler primarily reduces noise, while the resonator fine-tunes the exhaust system's sound by eliminating unwanted frequencies in a narrow range.
Conclusion
The exhaust system is an essential component of any internal combustion vehicle, ensuring exhaust gas discharge, noise reduction, and harmful emission control. Regular maintenance of the exhaust system, including checking the catalytic converter, particulate filter, and muffler, is crucial for maintaining engine health and protecting the environment.